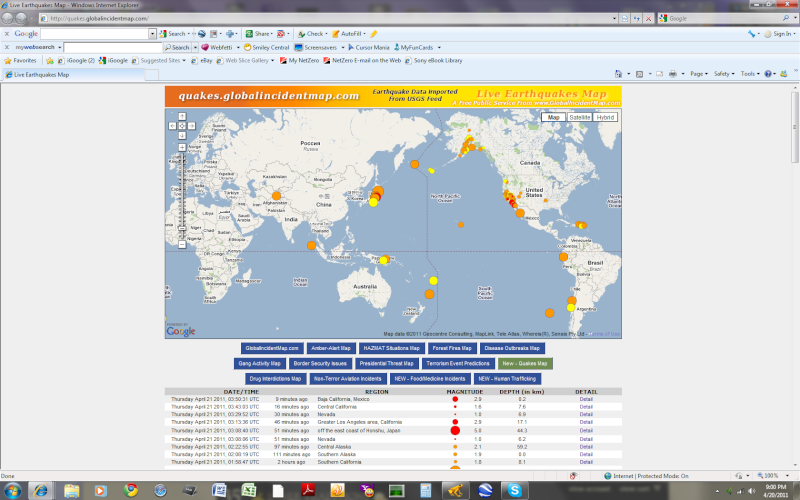
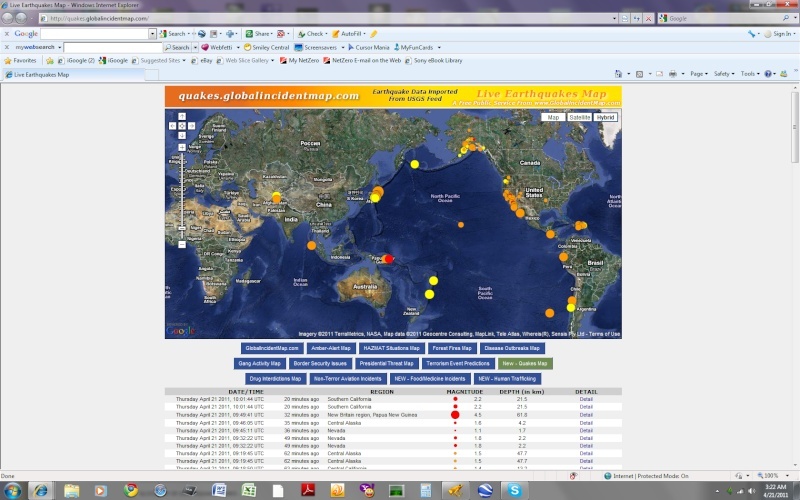
The Geysers have been quiet since last night. ?????????????
In general, activity at the Geysers seems to have decreased a bit in the last few days.
__________________
NOTE: Old Faithful (Calistoga, CA) often changes behavior before large quakes. I have not heard anything so far, but I have not looked, either.
TBC/TBA
_________________
Water for the Old Faithful Geyser of California comes from an underground river. When this water flows over the hot molten magma deep in the earth, it boils and expands and is collected in large cavities. Under tremendous pressure from the heat, and assisted by a constriction of the passage upward, the superheated water is forced through the fissures and fractures and erupts with an outpouring of steam followed by a fulmination of hot dancing water.
Under normal conditions, the water, the heat and the underground structure all remain constant and for this reason Old Faithful erupts regularly. Conditions which cause deviations from the normal pattern seem to relate to earthquakes.
The Old Faithful Geyser of California is proving itself a predictor of quakes.EarthquakesFrom two days to two weeks prior to an earthquake, the Old Faithful Geyser of California gives warning by delaying its regular performance from the average thirty minutes to a longer interval. During this prolonged interval, it may send up "splits," small eruptions to no more than two or three feet in height, every few minutes. Finally, after the long delay, a 60-foot column of water and steam shoots upward.
The Geyser will return to its normal pattern unless interrupted by further tectonic stresses. Several scientists have studied the Geyser and one scientist has set up an infrared heat detector nearby. When the Geyser erupts, the detector is activated and information is relayed into an office where a taped printout automatically records all the eruptions day and night. The scientists then can use such information to determine whether or not Old Faithful's digressions from normal behavior correlate with the advent of an earthquake, and records are kept for future comparisons. The earthquake activity is not located at the Geyser, but within 500 miles or more from the area.
A scientific study sponsored by the Carnegie Institution of Washington DC, is being conducted in order to document the possible correlation between the Geyser eruptions and earthquake activity.
http://www.oldfaithfulgeyser.com/information.html___________
Geysers and the Earth's Plumbing SystemsIntroduction
Geysers are essentially hot springs that become thermodynamically and hydrodynamically unstable. However, geysers are extremely rare on the surface of the earth, indicating that a complex set of parameters must be exactly right for geysers to occur. Figure 1 shows locations and Table 1 lists names of geyser fields of the world. It is worth noting that there are only approximately fifty geyser fields known to exist on earth and around two-thirds of those fifty contain five or fewer active geysers. Yellowstone National Park in Wyoming, U.S.A. has, by nearly an order of magnitude, more geysers than any other field known, and has been the site of extensive study of the properties and characteristics of geysers.
Because geysers are so rare, there have been several investigations into the conditions that must exist for geyser activity. It has been found that at least three essential conditions must be met, but there are many other contributing factors that influence the type and frequency of eruptions. The basic elements of a geyser are: 1) a water supply, 2) a heat source, and 3) a reservoir and associated plumbing system (Figure 2).
http://www.umich.edu/~gs265/geysers.htmlThere is a generally a strong correlation between earthquake activity and geyser behavior. This phenomena has been observed for centuries, but only recently have the changes in geyser behavior been documented. The 1959 Hegben Lake earthquake has had the most dramatic effect on Yellowstone geysers of any earthquake since the park's discovery (Rhinehart, 1980). Since the epicenter was so close to Yellowstone (only about 50 km away) the effects were significant. Immediately after the earthquake, all the geysers in the park erupted, and the average temperature in geysers and springs increased by an average of 2°C. Some geysers that were previously dormant became active, ostensibly by the opening of sealed channels along planes of weakness, and several active geysers changed their eruptive behavior. However, geyser response to earthquakes seems somewhat variable. Old Faithful in Yellowstone was the only geyser in the park that did not change its eruptive behavior after the Hegben Lake earthquake (Rhinehart, 1980). However, it has responded to several other earthquakes with epicenters much farther away, such as the magnitude 8.4 earthquake in Alaska in 1964. This indicates that the profound changes in geyser activity due to earthquakes are not due to slip along faults so much as by changes in regional strain. Since geysers record earthquake activity in a reasonably consistent manner, there have been several studies on whether geysers could be used as predictors for earthquake activity. Rhinehart (1980) states that in his detailed studies of geysers, there have been no systematic correlations between earthquakes and geyser activity. A more recent study by Silver and Valette-Silver (1992) showed that some geysers in California show changes in observable activity before nearby earthquake activity. They surmise that, although the response of geysers to tectonic strain is not well understood, there are two basic mechanisms by which seismic activity could affect geyser behavior. In the first, changes in the regional strain field change the volumetric flow velocity into the reservoir, thus affecting the interval between geyser eruptions. In another scenario, the permeability of the plumbing system could change due to strain-induced changes in microfractures in the geyser reservoir.