The tearing of Russia: 6.1 magnitude earthquake strikes southeast region of Russia

Lake Baikal: the mysterious rift of fire at 900 fanthoms?
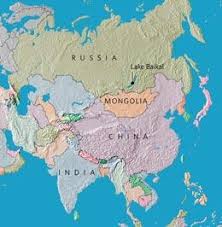
October 14, 2011 – RUSSIA - A 6.1 magnitude earthquake struck the Amurskay Oblast region of Southeast Russia at a depth of 15.3 km. The epicenter of the earthquake was 130 km (80 miles) SSW of Tynda, Russia and 5154 km (3202 miles) NE of MOSCOW, Russia. One hour and 15 minutes later, a 4.2 earthquake also struck near Lake Baikal- which is southwest of the epicenter. Lake Baikal was similarly hit by a 5.6 magnitude earthquake in July of 2011. The seismic turbulence in southeast Russia is happening along the periphery of a region of the Russia that is slowly tearing apart or rifting along a divergent plate boundary. Geological turbulence will only increase with time. Like Iceland, Africa and the sea-floor near El Hierro in the Canary Islands, this process appears to have become more excited this year and is an indication geological change is accelerating its advance across the world as the planet’s magnetic field strength continues to erode.Lake Baikal: the mysterious rift of fire at 900 fanthoms?
The Baikal Rift Zone is a divergent plate boundary centered beneath Lake Baikal in southeastern Russia. To its west is the Eurasian Plate and to its east is the Amur Plate which is moving away from the rift toward Japan at about 4 mm per year. As in all divergent plate boundary zones, the crust in the Baikal Rift Zone is thinning and magma is very close to the surface. Hot springs are present both on land and under Lake Baikal, although thus far, no evidence of actual volcanism has been found in the immediate vicinity of the lake. However, geologically-recent volcanic activity has occurred nearby and is probably associated with the Baikal Rift Zone. These volcanic centers are the Udokan Plateau, located about 400 km ENE of the northern tip of Lake Baikal, the Oka Plateau, located about 200 km WNW of the southwest tip of Lake Baikal, and the Vitim Plateau, around 200 km east of the rift. Besides the East African Rift, the Baikal Rift zone is the only other current example of a divergent plate boundary within continental crust on Earth. –Wikipedia

Lake Baikal is not only the deepest lake in the world (1,637 meters) — it is also the oldest freshwater lake. According to scientists, the lake is more than 25 million years old, and holds about 20% of the world’s surface freshwater. The world’s largest fresh water lake is mysteriously warming for unknown reasons and Dr. Lyubov, a Russian scientist, believes she knows why – climate change. Lyubov believes one of the world’s oldest bodies of water is intimately and inexplicably linked to changes going on in the environment which are accelerating the planet’s temperature. For example, her research team found that changes in Lake Baikal’s temperature varied along with monthly El Niño variations in the surface temperature of the Pacific Ocean thousands of miles away. The researchers also found connections between the jet stream and Lake Baikal. Changes in the jet stream’s strength and direction forecast seasonal changes in the lake by about three months. Overall they found the lake is also warming. The lake’s temperature even reflected decade-scale changes in the Earth’s speed of rotation.
Given Lake Baikal’s immense depth, we believe there can only be one thing capable of influencing the Southern Oscillation (El Niño) and impacting the planet’s rotation while contributing to the gradient rise in the Lake’s temperature and it is the most abundant viscous substance on planet Earth – it is magma. A rift is likely widening under the lake and though no volcanic activity has been specifically identified to date, hot springs are present both on land and deep under water. What is perhaps more well-known is the lake’s violent past seismic history. Multiple earthquakes shook the Lake Baikal region between December 30, 1861 and January 1, 1862, causing widespread panic and destruction, unleashing a tsunami of icy water that rolled over the Tsagan steppe, and left more than 200 square kilometers of land permanently underwater along with the homes and livestock of the Buriats who lived there. A 7.3 magnitude quake shook the lake in 2001 and a 6.3 quake struck at a depth of 10 km in 2008. Ice quakes were measured on the frozen surface of the lake by Russian scientists in 2008 and a 6.7 quake again struck the lake in September of 2010. Researchers have long theorized there may be a divergent plate boundary centered beneath Lake Baikal. To its west is the Eurasian Plate and to its east is the Amurian Plate which is moving away from the rift toward Japan at about 4 (maybe even up to 7) mm per year. GPS measurements indicate that the Amurian plate is slowly rotating counter-clockwise. We believe Lake Baikal will become more of a hazard zone as Earth-changes intensify.
Two women have dedicated their lives to protecting Russia's Lake Baikal, their research proves that the lake is warming at a rate three times faster than the air.
Their mission is to find new life forms and preserve existing ones.
Located in south west Siberia, the lake contains 20 percent of the Earth's fresh water and is being severely affected by global warming.
Al Jazeera's Jonah Hull reports.